Table of Contents
Data description
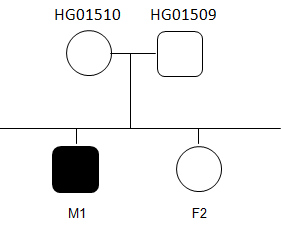
Working plan
We have several candidate profiles of mutations because it is clear the kind of mutation we are searching but sometimes we do not have a specific clues.
How many variants do you detect for each scenario?
A. Individual filters
- Recessive heritage
- Dominant heritage (father is affected).
- For this region: 1:1000-50000
- For this gene: BRD9
- For these genes at the same time: BRD9,CDK11A,RET
- Description of variants. How many SNVs and INDELs can you search?
- Variants with MAF (Minimum Allelic Frequency) < 0.1 for all populations in 1000 Genomes phase 3
- Variants with MAF (Minimum Allelic Frequency) < 0.01 for all populations in 1000 Genomes phase 3
- Variants with MAF (Minimum Allelic Frequency) < 0.001 for all populations in 1000 Genomes phase 3
B. Progressive selection
- We have several clues about our candidate variants. In addition of knowing the pattern of recessive heritage, we search variants with MAF < 0.1 (for all populations in 1000 Genomes phase 3) because it is a rare disease. Consequence type must be “synonymous variant”
- How many variants do you have including both characteristics?
- We have several clues about our candidate variants. In addition of knowing the pattern of dominant heritage (father is affected), we search variants with MAF < 0.1 (for all populations in 1000 Genomes phase 3) because it is a rare disease. Consequence type must be “synonymous variant”
- How many variants do you have including both characteristics?