Table of Contents
Exercise 7
Data description
Working plan
If we have a clear profile of mutation, we will have to apply these filters on BiERapp to get directly the possible causal mutation. Sometimes we have several interesting profiles of mutations, not only one. For this case we should explore these different scenarios and decide the best prioritization strategy.
To know better this web tool, we propose you two groups of activities:
- In the part A of this activity, we would have to apply individual filters. This action give us information about the effect of each filter (maybe there are some filters more powerful than other). After each filtering, we have to clear the filter to apply the next one.
- In the part B of this exercise, we have a real selection where we combine several filters at the same time. It is interesting to know how the number of variants is reducing, when applying a progressive group of filters (without deleting the previous filter). We want to know the accumulative effect of several filters (all together).
How many variants do you detect for each scenario?
A. Individual filters
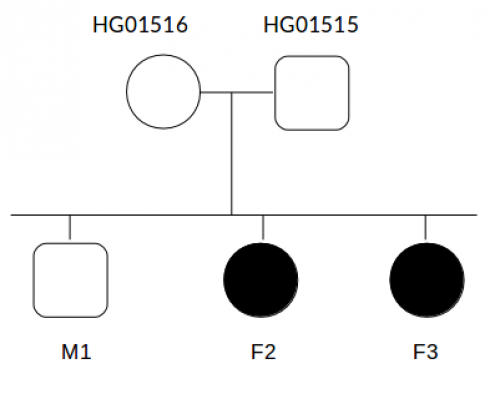
A.1. Select only these 4 individuals: mother, father and daugthers F2, F3
- Total number of variants without filters
- Recessive heritage
- Dominant heritage (mother is affected).
- Evaluate these regions at the same time: 3:10000-500000, 5:1000-500000, 13:500-100000
- For theses genes related to Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: BSCL2, DNM2, EGR2, FGD4, FIG4, GARS, GDAP1, GJB1, HSPB1, HSPB8, KIF1B, LITAF, LMNA, MFN2, MPZ, MTMR2, NDRG1, NEFL, PMP22, PRPS1, PRX, RAB7A, SBF2, SH3TC2, TRPV4, and YARS
A.2. Now select all familiy (5 individuals)
The same filters for whole family:
- Total number of variants without filters
- Recessive heritage
- Dominant heritage (mother is affected).
- Evaluate these regions at the same time: 3:10000-500000, 5:1000-500000, 13:500-100000
- For theses genes related to Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: BSCL2, DNM2, EGR2, FGD4, FIG4, GARS, GDAP1, GJB1, HSPB1, HSPB8, KIF1B, LITAF, LMNA, MFN2, MPZ, MTMR2, NDRG1, NEFL, PMP22, PRPS1, PRX, RAB7A, SBF2, SH3TC2, TRPV4, and YARS
A.3. Are there changes between two scenarios by different filters?
B. Progressive selection
- We have several clues about our candidate variants for the whole family (5 individuals):
- Recessive heritage
- For chromosome 1
- Save this information in a csv file
- Repeat the previous activity when having this family composition: father, mather and two daugthers:
- Recessive heritage
- For chromosome 1
- Save this information in a csv file
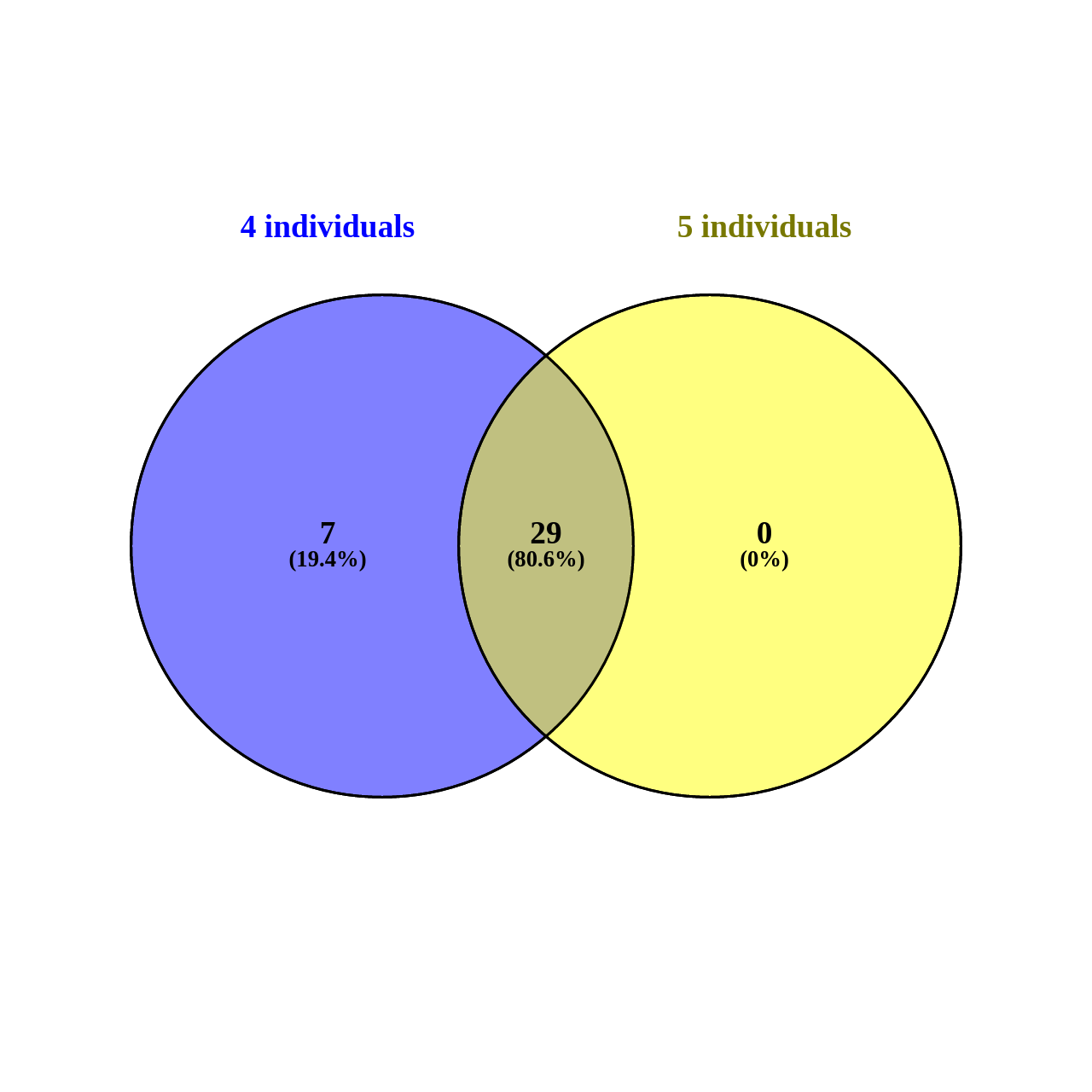
- Visualize the intersection between two previous groups of results from Venny web tool. Could you download this image?
Solutions
Some of these solutions could be different when having updated databases
A. Individual filters
A.1. Select only these 4 individuals: mother, father and daugthers F2, F3
- Total number of variants without filters: 39998
- Recessive heritage: 425
- Dominant heritage (mother is affected): 3840
- Evaluate these regions at the same time: 3:10000-500000,5:1000-500000,13:500-100000: 31
- For theses genes related to Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: BSCL2, DNM2, EGR2, FGD4, FIG4, GARS, GDAP1, GJB1, HSPB1, HSPB8, KIF1B, LITAF, LMNA, MFN2, MPZ, MTMR2, NDRG1, NEFL, PMP22, PRPS1, PRX, RAB7A, SBF2, SH3TC2, TRPV4, and YARS: 54
A.2. Now select all familiy (5 individuals)
- Total number of variants without filters: 39998
- Recessive heritage: 321
- Dominant heritage (mother is affected): 1161
- Evaluate these regions at the same time: 3:10000-500000, 5:1000-500000, 13:500-100000: 31
- For theses genes related to Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: BSCL2, DNM2, EGR2, FGD4, FIG4, GARS, GDAP1, GJB1, HSPB1, HSPB8, KIF1B, LITAF, LMNA, MFN2, MPZ, MTMR2, NDRG1, NEFL, PMP22, PRPS1, PRX, RAB7A, SBF2, SH3TC2, TRPV4, and YARS: 54
A.3. Are there changes between two scenarios by different filters?
- There are changes for filters 2,3, not for 4 and 5.
B. Progressive selection
- We have several clues about our candidate variants for the whole family (5 individuals):
- Recessive heritage: 321
- For chromosome 1: 29
- Save this information in a csv file
- Repeat the previous activity when having this family composition: father, mather and two daugthers:
- Recessive heritage: 425
- For chromosome 1: 36
- Save this information in a csv file
- Visualize the intersection between two previous groups of results Venny web tool